16 |
OilfieldTechnology
February
2014
noisecausedbyroughweatherconditions.Towingatgreaterdepths
improvesthe low‑frequencycontentandbenefitsfromaquieter
environment,buttothedetrimentof losingthehighfrequencycontent.
Thisfrequencyattenuation is inherenttoalltowed‑streamer
acquisitiontechniques,and isreferredtoastheghostnotcheffect.
It iscausedbythereflectionofseismicenergyfromtheseasurfacea
shortdistanceabovethestreamers,which interfereswiththeuseful
seismicsignal.Theghosteffectoccursatboththesourceandreceiver
side.Therangeoffrequencies impacted isdependentuponthedepth
ofdeployment.Anumberofacquisitionandprocessingmethodshave
beendevelopedtoaddresstheghosteffect,andrecoverawiderrange
offrequencies.Thesemethods,commonlydescribedas ‘broadband
solutions’, includeacquisitionconfigurationssuchas ‘over/under’ (inwhich
pairsofstreamersaretowedatdifferentdepths),slantedstreamersand
dual‑measurementstreamers.
However,achievinghigh‑resolution imagingrequiresbroadband
data inatruly3Dsense–notonlytemporallybutalsospatially.Anew
technologyhasbeen introducedtothemarketplacethat isableto
addressboththetemporalandspatialbandwidthconstraints,enabling
full3Dprocessingcapabilitiesthatgowellbeyondwhat istraditionally
understoodasbroadband.
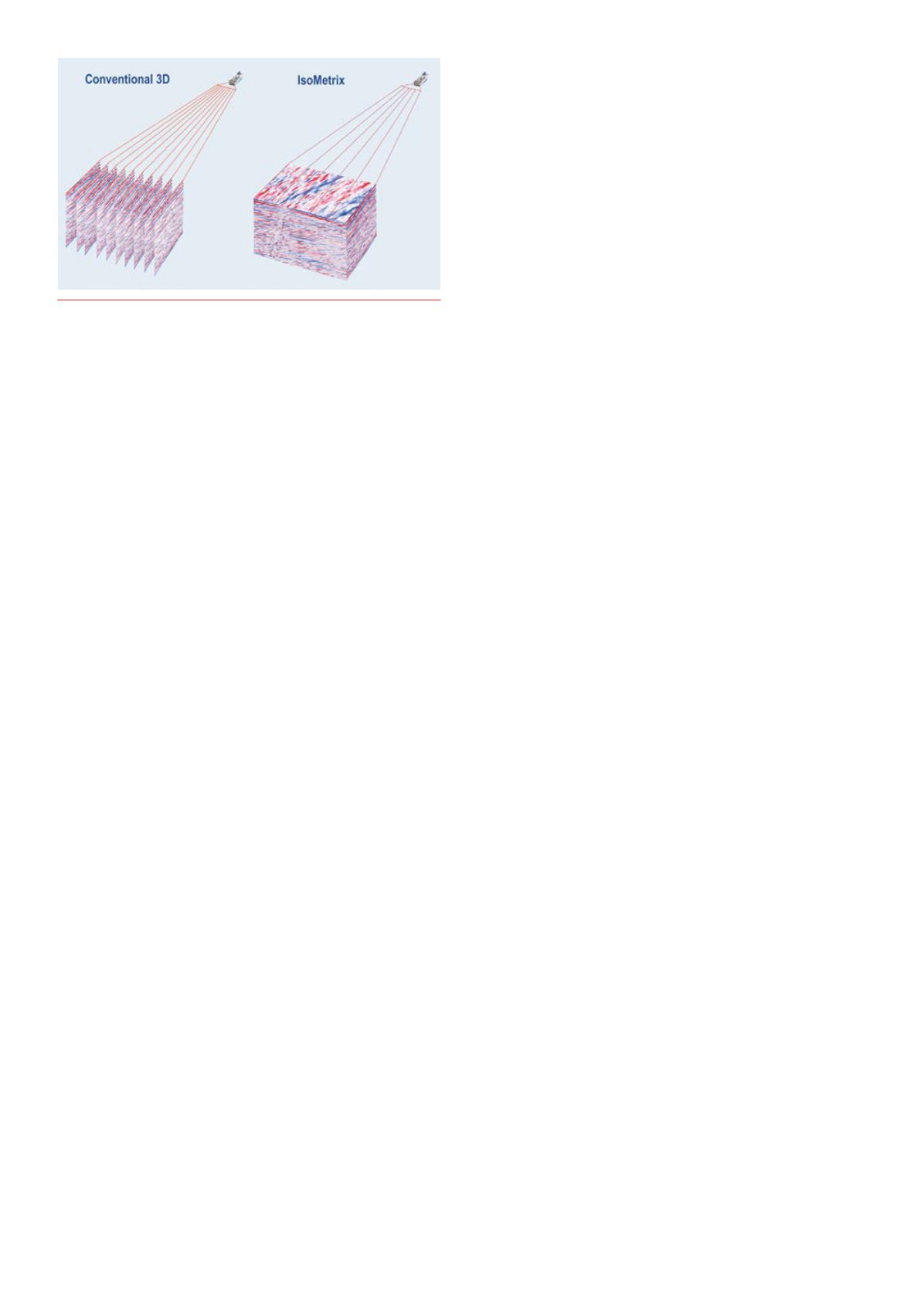
Spatialresolutionin3D
3Dseismicsurveysaretypicallyacquiredbyavesselequippedwith
between8and16streamerscontaininghydrophonesensors.Spatial
samplingofthedatarecordedalongeachstreamercanbeasfineas
3.125m;however,thestreamersareusuallytowed50to100mapart.
Themuchgreaterdistancebetweenadjacentstreamersmeansthat
sampling inthecrosslinedirectioncanbe16‑32timessparser.Such
coarselysampleddatacannotcapturethefullcomplexityofthe3Dseismic
wavefield,thus limitingtheabilitytooptimally imagethesubsurface
(Figure1).
Recentdevelopmentsnowmake itpossibletodeliveratruly
isometricwavefield. Isometricreferstoanequallysampledwavefieldboth
alongandbetweenthestreamers.This isenabledby IsoMetrixmarine
isometricseismictechnology,developedbyWesternGeco. Itutilisesa
newgenerationofmultimeasurementtowedstreamer,combinedwith
advancedcomputeralgorithms,todeliverthefull3Dbroadbandseismic
wavefieldsampledona6.25mx6.25msurfacegrid.
Trueisometric3Dsampling
Thenewcategoryofmarineseismicacquisition isenabledbythe
Nessie‑6point‑receiverstreamersystem,whichcombineshydrophones
withcalibratedaccelerometersthatmeasureparticleacceleration inthe
seismicwavefield.Measuringacceleration intwodirectionsprovides
direct informationonthepressuregradientandenablesunaliased
reconstructionof thepressurewavefieldbetweenstreamers.Foreach
seismicshotrecord, themeasuredpressure (P),vertical (Z),andcrossline
horizontal (Y)componentsof thepressuregradientsarecombinedusing
adata‑dependentprocessingtechniquecalledgeneralisedmatching
pursuit (GMP).TheGMPschemeprovidesaspatialdealiasingcapability
ofmuchhigherordersthanpredictedbyclassicalsignalsampling
theory,andalsosimultaneouslydeghoststhedata inatrue3D fashion.
Thesource‑sideghostcanbesimultaneouslyaddressedusingthe
WesternGecoDeltasource familyofcalibratedmarinebroadband
seismicsources.
Explorationefficiency
Theeconomicsofaseismicsurveyarestrongly influencedbythearea
ofsubsurfacecoveragepersail line.This isespeciallytrue in large‑scale
explorationplays.Widerspreads increasearealcoverageandhence
reducetotalacquisitiontime–butthisapproachhas limitations.Asnoted
previously,towingconventionalstreamersat largeseparationsfurther
compromisesthecrosslinespatialresolution.Addingmorestreamers
mitigatesthe loss inresolutionbutaddstothecomplexityofacquisition
operations.Thecombinationofmultimeasurementstreamersandthe
GMPalgorithmmeansthat IsoMetrixdatacanbeacquiredwithrelatively
widestreamerseparationwithoutcompromisingresolution.Thishasthe
potentialtoreduceacquisitionduration.
Inorderto increasespatialsampling inthecrosslinedirection,
conventionalsurveysoftendeployvesselswithdualsourcesoperating
sequentially in ‘flip‑flop’mode.Adisadvantageofthistechnique isthat
it increasesthedistancebetweenadjacentshotsandreducesspatial
sampling inthereceiverandcommonmidpoint(CMP)domains,which
cancompromisedataquality.Through itsabilitytoreconstructtheseismic
wavefieldbetweenstreamers,thenew isometrictechnologyovercomes
thiscompromise,achievingdataproperlysampled inalldomainsfroma
vesseltowingasinglesource.
Further increases inefficiencyforexplorationsurveyscanberealised
byemployingmultiplevessels.Forexample,asecondsourcecanbe
deployedfromanothervessel,positionedtodoublethearealcoverage. In
effect,thishalvesthenumberofsail lines–andhencethetime–required
tocompletethesurvey.Thesecondvessel istypicallyasmallerboat,which
operatesatsignificantly lowercostthanaspecialistrecordingvessel.
Althoughthisformofdesigncanbeenvisagedforconventionalacquisition
streamers, it introducesextracompromises inresolutionandsampling in
differentdomains.An IsoMetrixsystemcanachievethesameefficiencies
withoutcompromisinggeophysical integrity.Thistechnique isparticularly
appropriateforexploration indeepwaterenvironments,wheretheseabed
canbecorrectly imageddespitethe longerminimumsource‑receiver
offsets inherenttomulti‑vesseloperations.
Repeatability
Time‑lapse(4D)projectsacquire3Dsurveysat intervalsbeforeand
duringreservoirproduction.Therepeatdatasetsareanalysedtomap
subtlechangesovertime intheseismicresponseofareservoircausedby
changes inpressureorfluidcontent. Informationfromthistechnique is
oftenusedtoguidereservoirmanagementdecisions, identifyflowbarriers
and locateuntappedcompartmentsfor infilldrilling.
Differences inthepositioningofseismicequipmentbetweensurveys
isalmost inevitablegiventhechangingseaandweatherconditions,plus
thedevelopmentoffield infrastructureacrossmanyyears.Thesecan
leadtoartifacts inthe4Danalysisthatmaskthetruevariationscaused
byreservoirfluidmovements.Minimisingsuchdifferencesequatesto
improvedrepeatabilityandclearer,morereliable,4Danalysis.
Figure1.
Conventional3Dsurveysaretypicallyacquiredbyavessel
equippedwithstreamerstowed50to100mapart, leadingtosparse
sampling inthecrosslinedirection. IsoMetrixtechnologyenables
reconstructionofthefull3Dwavefieldbetweenthestreamers. Image
courtesyofWesternGeco.


